Cisco Certification Exam Prep Materials
Cisco CCNA Exam Prep Material Download
Cisco CCT Exam Prep Material Download
- Cisco 010-151 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 100-490 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 100-890 Dumps PDF
- Tips: Beginning February 10, the CCT Certification 500-150 FLDTEC v1.0 exam will replace the 100-490, 010-151, and 100-890 exams.
Cisco CyberOps Exam Prep Material Download
Cisco DevNet Exam Prep Material Download
Cisco CCNP Exam Prep Material Download
- Cisco 300-410 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-415 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-420 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-425 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-430 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-435 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-440 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-510 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-515 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-535 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-610 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-615 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-620 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-630 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-635 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-710 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-715 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-720 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-725 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-730 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-735 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-810 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-815 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-820 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-835 Dumps PDF
Cisco CCIE Exam Prep Material Download
- Cisco 350-401 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 350-501 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 350-601 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 350-701 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 350-801 Dumps PDF
Cisco CCDE Exam Prep Material Download
Cisco Other Exam Prep Material Download
- Cisco 500-052 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-210 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-220 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-420 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-442 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-444 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-470 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-490 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-560 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-710 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-150 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-750 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-760 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-765 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-805 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-821 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-826 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-846 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-905 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 820-605 Dumps PDF
Fortinet Exam Dumps
fortinet nse4_fgt-6.4 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse4_fgt-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse5_faz-6.4 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse5_faz-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse5_fct-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse5_fmg-6.4 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse5_fmg-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse6_fml-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse6_fnc-8.5 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse7_efw-6.4 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse7_efw-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse7_sac-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse7_sdw-6.4 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse8_811 dumps (pdf + vce)
We have updated 300-410 dumps, which are the 300-410 ENARSI study materials that will surprise you.
If you need to take the Cisco CCNP 300-410 (ENARSI) exam and excel in the 300-410 exam, then you should find 300-410 dumps learning resources that can help you overcome your weaknesses.
Go to the webpage for 300-410 dumps >> https://www.pass4itsure.com/300-410.html Reliable learning materials with 548 real exam questions and answers to help you pass the 300-410 ENARSI exam.
How much do you know about the 300-410 ENARSI exam?
The so-called knowing oneself and knowing the other can win every battle. First of all, we need to understand the Cisco 300-410 exam:
Abbreviation: Cisco ENARSI
Full name: Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)
Certification: CCNP Enterprise
Official Cisco training: Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)
Exam duration: 90 minutes
Cost: $300, (plus tax or use Cisco Learning Credit)
Languages: English and Japanese
How do I get CCNP Enterprise?
To receive the CCNP Enterprise Award, you need to pass two exams: a core exam and an enterprise concentration exam of your choice. 300-410 ENARSI is an intensive exam that requires not only passing but also core exam 350-401 to fully achieve CCNP Enterprise certification.

The list of all exams for CCNP Enterprise certification is shown in the figure below:

After understanding the exam, how to prepare for the 300-410 exam next?
First, you need the right learning material to help, and the Pass4itSure 300-410 dumps are the right ones. It provides all the questions and answers needed for the exam.
Second, you need a lot of practice to master the knowledge points with the help of 300-410 dumps of questions and answers.
Free Cisco 300-410 dumps practice test online resource sharing (1-13)
QUESTION # 1
Earlier today you created and applied an access list designed to restrict remote access to the router R62 ONLY from the device at 2001:DB8:0:4:: 32. During testing, you discover that it is not having the desired effect. You execute the show run command and see the following partial output that is relevant to the issue:

Why is the access list not functioning correctly?
A. the IPv6 address in the list is not formatted correctly
B. the list is not applied to the proper interface
C. the list is missing a deny statement
D. the ipv6 access-group command should be used to apply the list
Correct Answer: B
The list is applied to the wrong interface. An access list that is designed to control remote access should be applied to the VTY lines, not to one of the physical interfaces. If the command were formatted correctly, the show run output would appear as follows:
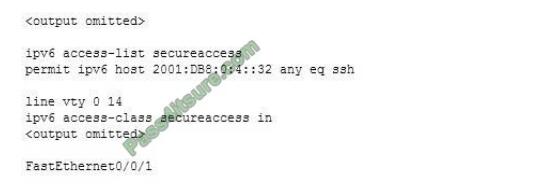
The IPv6 address is formatted correctly. Although it has been shortened in format, it follows all of the shortening rules. It omits only leading zeros and it utilizes the double colon only once. The access list does not require a deny statement. There is an implicit deny all at the end of the list. The ipv6 access-group command should not be used to apply the list. This command is used when an access list is
applied to a physical interface, not the VTY lines.
Objective:
Infrastructure Security
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify router security features
References:
Cisco > IPv6 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.0S > Implementing Traffic Filters and Firewalls for IPv6 Security > Access Control Lists for IPv6 Traffic Filtering Cisco > Security Configuration Guide: Access Control Lists, Cisco IOS Release 15S > Controlling Access to a Virtual Terminal Line
QUESTION # 2
Refer to the exhibit.
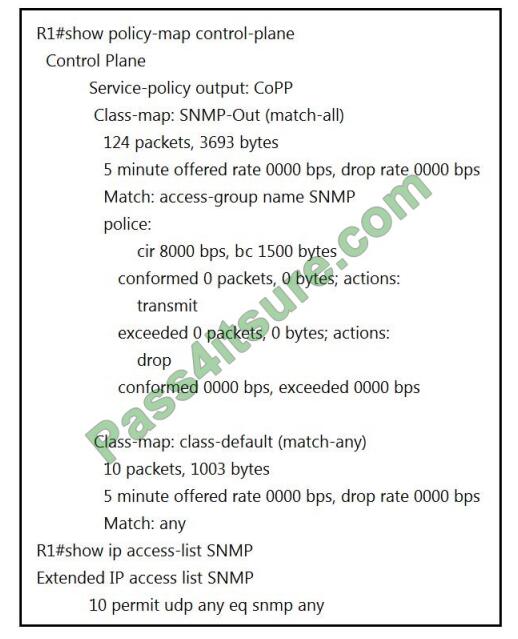
R1 is being monitored using SNMP and monitoring devices are getting only partial information. What action should be taken to resolve this issue?
A. Modify the CoPP policy to increase the configured exceeded limit for SNMP.
B. Modify the access list to include snmptrap.
C. Modify the CoPP policy to increase the configured CIR limit for SNMP.
D. Modify the access list to add a second line to allow udp any any eq snmp.
Correct Answer: D
QUESTION # 3
Refer to the exhibit. Jun 24 08:54:51.530: IF-EvO(GigabitEthemet0/0): IP Routing reports state transition from DOWN to DOWNJun 24 08:54:52.525: %1INEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthemet0/0, changed state to downJun 24 08:54:52.528: IF-EvD(GigabitEthernet0/0): IP Routing reports state transition from DOWN to DOWNJun 24 08:54:53 215: IF-EvD(GigabitEthernet0/0): IP Routing reports state transition from DOWN to DOWNJun 24 08:54:54.998:
%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthemet0/0, changed state to upJun 24 08:54:55.006: IFEvO(GigabitEthernet0/0): IP Routing reports state transition from DOWN to UPJun 24 08:54:55.998:
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
R1 is connected with R2 via GigabitEthernet0/0, and R2 cannot ping R1. What action will fix the issue?
A. Fix route dampening configured on the router
B. Replace the SFP module because it is not supported.
C. Fix IP Event Dampening configured on the interface.
D. Correct the IP SLA probe that failed.
Correct Answer: C
The IP Event Dampening feature introduces a configurable exponential decay mechanism to suppress the effects of excessive interface flapping events on routing protocols and routing tables in the network. This feature allows the network operator to configure a router to automatically identify and selectively dampen a local interface that is flapping.
QUESTION # 4
Which of the following does the show ip eigrp topology all-links command display?
A. Only feasible successors
B. Only non-feasible successors
C. Both feasible successors and non-feasible successors
D. Both successors and feasible successors
Correct Answer: C
The show ip eigrp topology all-links command displays both the feasible successors and the non-feasible successors. Feasible successors refer to backup routes to a particular destination network. Routers compute the metric/distance of every route they learn from their EIGRP neighbors.
There can be multiple routes to the same destination network. The route with the least metric value to a specific destination network is selected as the best path, or successor, to that network. However, if the successor goes down, the router computes the next best loop-free path to the same destination network, which is called the feasible successor.
Feasible successors must have a reported (or advertised) distance that is less than the feasible distance, or current best metric. The routes that are neither successors nor feasible successors are called non-feasible successors. The feasible successors and the non-feasible successors can be viewed by running the show ip eigrp topology all-links command.
Sample output is shown below:
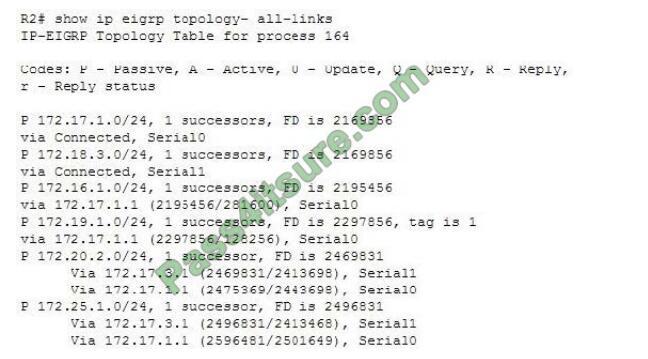
The router at 172.17.3.1 is directly connected to three networks: 172.25.1.0/24, 172.20.2.0/24, and 172.18.2.0/24. The second network, 172.20.2.0/24, is listed as the source of the successor routes to those networks.
The connection to the last network, 172.18.2.0/4, can deduced by the fact that the local router uses the Serial1 interface to connect to the two networks that the router at 172.17.3.1 is a successor for. Therefore, that router must be directly connected to the network on the Serial1 interface of the local router.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify policy-based routing
References:
Cisco IOS IP Routing: EIGRP Command Reference > show ip eigrp topology
QUESTION # 5
Refer to the exhibit. Which action restores OSPF adjacency between R1 and R2?
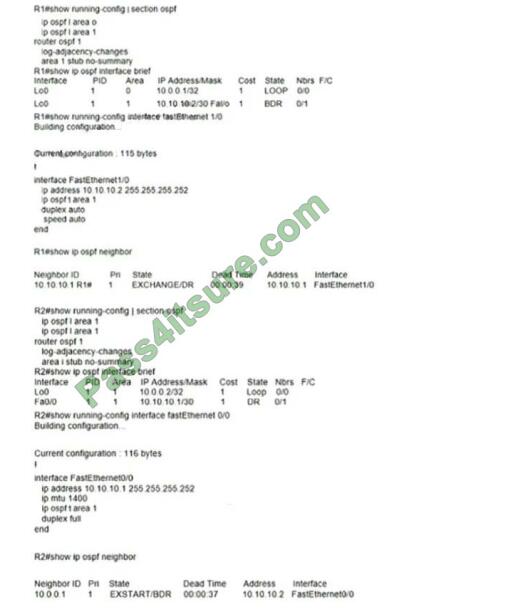
A. Change the IP MTU of R1 Fa1/0 to 1300
B. Change the IP MTU of R2 Fa0/0 to 1300
C. Change the IP MTU of R1 Fa1/0 to 1500
D. Change the IP MTU of R2 Fa0/0 to 1500
Correct Answer: D
QUESTION # 6
Which protocol does VRF-Lite support?
A. S-IS
B. ODR
C. EIGRP
D. IGRP
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION # 7
Refer to the exhibit. Users report that IP addresses cannot be acquired from the DHCP server. The DHCP server is configured as shown. About 300 total nonconcurrent users are using this DHCP server, but none of them are active for more than two hours per day. Which action fixes the issue within the current resources?
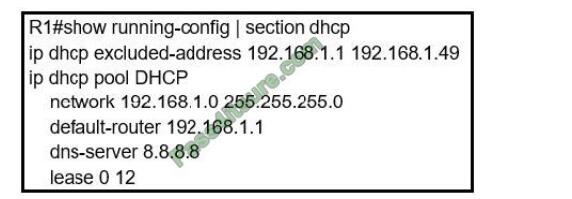
A. Modify the subnet mask to the network 192.168.1.0 255.255.254.0 command in the DHCP pool
B. Configure the DHCP lease time to a smaller value
C. Configure the DHCP lease time to a bigger value
D. Add the network 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 command to the DHCP pool
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION # 8
Which parameter does EIGRP use to compute the bandwidth part of the metric?
A. The maximum bandwidth link in the path, in kilobits per second
B. The minimum bandwidth link in the path, in kilobits per second
C. The average bandwidth of all the links in the path, in kilobits per second
D. The average bandwidth of all the links in the path, in kilobytes per second
Correct Answer: B
The minimum bandwidth link, in kilobits per second, is used in the EIGRP metric calculation, because this is the limiting factor in the overall speed of delivery over the path.
BW = (10,000,000 / bandwidth in Kbps) x 256
Delay = (delay in microseconds / 10) x 256
The formula for calculating the EIGRP metric is shown below:
[K1 x BW + (K2 X BW) / (256 – load) + K3 x delay] X [K5 / (reliability + K4)]
You should note, however, that when K5 = 0 (as it is by default), a slightly different formula applies.
When K5 = 0, the EIGRP metric is [K1 X BW + (K2 X BW) / (256 – load) + K3 x delay]
By default, K1 = 1, K3 = 1, and K2, K4, and K5 = 0.
Therefore, the default EIGRP metric is BW + Delay, where “BW” and “Delay” are determined according to the formula above. The final formula is shown below:
[10,000,000 / (bandwidth in Kbps) + (delay in microseconds) / 10] * 256
These usually are derived from the values listed in the show interfaces command.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Describe and optimize EIGRP metrics
References:
Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP Routing > Technology Information > Technology White Paper > Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol > Using The Metrics
QUESTION # 9
Refer to the exhibit.
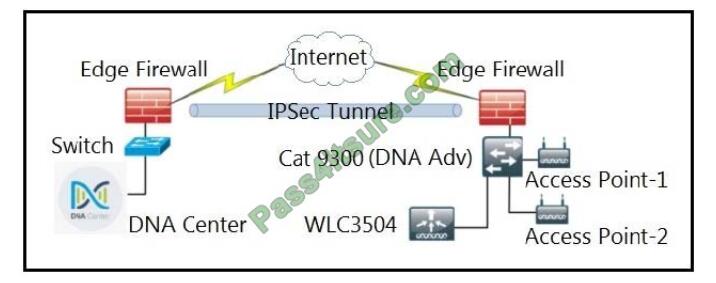
A network administrator is discovering a Cisco Catalyst 9300 and a Cisco WLC 3504 in Cisco DNA Center. The Catalyst 9300 is added successfully. However, the WLC is showing error “uncontactable” when the administrator tries to add if in Cisco DNA Center. Which action discovers WLC in Cisco DNA Center successfully?
A. Delete the WLC 3504 from Cisco DNA Center and add it to Cisco DNA Center again.
B. Add the WLC 3504 under the hierarchy of the Catalyst 9300 connected devices.
C. Copy the .cert file from the Cisco DNA Center on the USB and upload it to the WLC 3504.
D. Copy the .pem file from the Cisco DNA Center on the USB and upload it to the WLC 3504.
Correct Answer: D
QUESTION # 10
R2 has a locally originated prefix 192.168.130.0/24 and has these configurations: What is the result when the route-map OUT command is applied toward an eBGP neighbor R1 (1.1.1.1) by using the neighbor 1.1.1.1 route-map OUT out command?

A. R1 sees 192.168.130.0/24 as two AS hops away instead of one AS hop away.
B. R1 does not accept any routes other than 192.168.130.0/24
C. R1 does not forward traffic that is destined for 192.168.30.0/24
D. Network 192.168.130.0/24 is not allowed in the R1 table
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION # 11
Refer to the following diagram of an OSPF network.
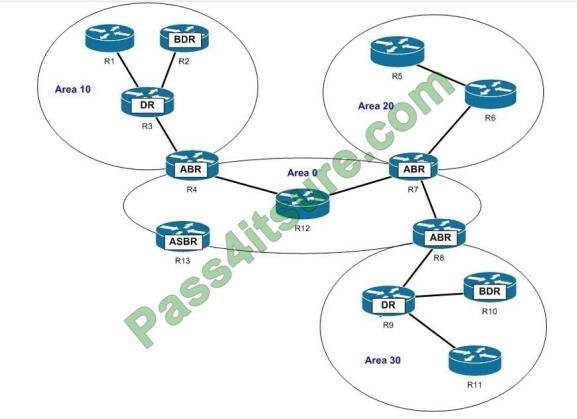
Which of the following routers generate network link advertisements (NLA)? (Choose all that apply.)
A. R3
B. R4
C. R7
D. R8
E. R9
F. R13
Correct Answer: AE
The R3 and the R9 routers in the scenario generate network link advertisements (NLA). An NLA or a Type 2 LSA is generated only by the designated router (DR) of a segment. Type 2 LSAs are generated only for those networks in which a DR has been selected. A DR is a router that has the highest OSPF priority on a segment. Until there are two OSPF routers on the segment, no Type 2 LSAs will be generated.
Type 2 LSAs are flooded in the area that contains the network segment with the DR. These advertisements are used by the DR to represent the routers that are connected to the network. This type of LSA is sent to those routers that belong to the same network as the DR. Therefore, in this case, Type 2 LSAs are generated by the R3 and the R9 routers. R3 sends the LSAs to R1, R2, and R4, while R9 sends LSAs to R8, R10, and R11.
R4, R7, or R8 will not send NLAs or Type 2 LSAs. These three routers are area border routers (ABR) for different OSPF areas. Like any other OSPF router, these routers generate Type 1 LSAs or router link advertisements (RLA). The LSAs contain the state of the routers that belong to same area.
In this case, R4 generates and floods Type 1 LSAs into Area 0 and Area 10. Similarly, R7 and R8 flood Type 1 LSAs into Area 0 and Area 20, and Area 0 and Area 30, respectively. ABRs also generate Type 3 and Type 4 LSAs or summary link advertisements (SLA). These LSAs are flooded into other areas to and from the backbone area. Type 3 LSAs contain the list of networks that are exchanged between two areas.
In this case, R4 floods Type 3 LSAs into Area 0 and Area 10; R7 floods these LSAs into Area 0 and Area 20; and R8 floods them into Area 0 and Area 30. Type 4 LSAs list the routes that point to autonomous system boundary router (ASBR).
R13 will not generate Type 2 LSAs. R13 is an Area System Border Router (ASBR), which generate Type 5 LSAs apart from Type 1 LSAs. Type 5 LSAs, or external link advertisements, list the routes external to the AS; they are flooded throughout the OSPF domain except for stub areas.
Objective:
Layer 3 Technologies
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify network types, area types, and router types
References:
Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Routing > Technology Information > Technology Whitepaper > OSPF Design Guide
QUESTION # 12
What are the two prerequisites to enable BFD on Cisco routers? (Choose two)
A. A supported IP routing protocol must be configured on the participating routers.
B. OSPF Demand Circuit must run BFD on all participating routers.
C. ICMP must be allowed on all participating routers.
D. UDP port 1985 must be allowed on all participating routers.
E. Cisco Express Forwarding and IP Routing must be enabled on all participating routers.
Correct Answer: AE
QUESTION # 13
Refer to the exhibit.
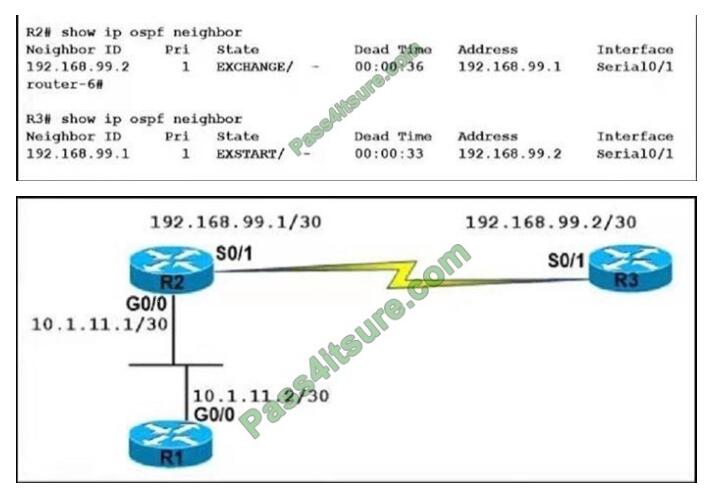
An OSPF neighbor relationship between R2 and R3 is showing stuck in EXCHANGE/EXSTART state. The neighbor is established between R1 and R2. The network engineer can ping from R2 to R3 and vice versa, but the neighbor is still down. Which action resolves the issue?
A. Restore the Layer 2/Layer 3 conectivity issue in the ISP network.
B. Match MTU on both router interfaces or ignore MTU.
C. Administrative “shut then no shut” both router interfaces.
D. Enable OSPF on the interface, which is required.
Correct Answer: B
To read 548+ 300-410 questions, please visit this website.
Free online download of 300-410 dumps question answers (PDF) 1-13: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1dzQaef3ymVWDCrpVHx_rIA29DDvwB8Ro/view?usp=sharing
Written by Ralph K. Merritt
We are here to help you study for Cisco certification exams. We know that the Cisco series (CCNP, CCDE, CCIE, CCNA, DevNet, Special and other certification exams are becoming more and more popular, and many people need them. In this era full of challenges and opportunities, we are committed to providing candidates with the most comprehensive and comprehensive Accurate exam preparation resources help them successfully pass the exam and realize their career dreams. The Exampass blog we established is based on the Pass4itsure Cisco exam dump platform and is dedicated to collecting the latest exam resources and conducting detailed classification. We know that the most troublesome thing for candidates during the preparation process is often the massive amount of learning materials and information screening. Therefore, we have prepared the most valuable preparation materials for candidates to help them prepare more efficiently. With our rich experience and deep accumulation in Cisco certification, we provide you with the latest PDF information and the latest exam questions. These materials not only include the key points and difficulties of the exam, but are also equipped with detailed analysis and question-answering techniques, allowing candidates to deeply understand the exam content and master how to answer questions. Our ultimate goal is to help you study for various Cisco certification exams, so that you can avoid detours in the preparation process and get twice the result with half the effort. We believe that through our efforts and professional guidance, you will be able to easily cope with exam challenges, achieve excellent results, and achieve both personal and professional improvement. In your future career, you will be more competitive and have broader development space because of your Cisco certification.
Categories
2025 Microsoft Top 20 Certification Materials
- Microsoft Azure Administrator –> az-104 dumps
- Microsoft Azure Fundamentals –> az-900 dumps
- Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure –> dp-203 dumps
- Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure –> az-204 dumps
- Microsoft Power Platform Developer –> pl-400 dumps
- Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution –> ai-102 dumps
- Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst –> pl-300 dumps
- Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions –> az-400 dumps
- Microsoft Azure Security Technologies –> az-500 dumps
- Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect –> sc-100 dumps
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Customer Engagement Apps (CRM) –> mb-910 dumps
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Finance and Operations Apps (ERP) –> mb-920 dumps
- Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals –> dp-900 dumps
- Microsoft 365 Fundamentals –> ms-900 dumps
- Microsoft Security Compliance and Identity Fundamentals –> sc-900 dumps
- Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals –> ai-900 dumps
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Solution Architect –> mb-700 dumps
- Microsoft 365 Certified: Enterprise Administrator Expert –> ms-102 dumps
- Microsoft 365 Certified: Collaboration Communications Systems Engineer Associate –> ms-721 dumps
- Endpoint Administrator Associate –> md-102 dumps

