Cisco Certification Exam Prep Materials
Cisco CCNA Exam Prep Material Download
Cisco CCT Exam Prep Material Download
- Cisco 010-151 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 100-490 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 100-890 Dumps PDF
- Tips: Beginning February 10, the CCT Certification 500-150 FLDTEC v1.0 exam will replace the 100-490, 010-151, and 100-890 exams.
Cisco CyberOps Exam Prep Material Download
Cisco DevNet Exam Prep Material Download
Cisco CCNP Exam Prep Material Download
- Cisco 300-410 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-415 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-420 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-425 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-430 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-435 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-440 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-510 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-515 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-535 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-610 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-615 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-620 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-630 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-635 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-710 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-715 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-720 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-725 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-730 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-735 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-810 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-815 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-820 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 300-835 Dumps PDF
Cisco CCIE Exam Prep Material Download
- Cisco 350-401 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 350-501 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 350-601 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 350-701 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 350-801 Dumps PDF
Cisco CCDE Exam Prep Material Download
Cisco Other Exam Prep Material Download
- Cisco 500-052 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-210 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-220 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-420 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-442 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-444 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-470 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-490 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-560 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 500-710 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-150 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-750 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-760 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-765 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-805 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-821 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-826 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-846 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 700-905 Dumps PDF
- Cisco 820-605 Dumps PDF
Fortinet Exam Dumps
fortinet nse4_fgt-6.4 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse4_fgt-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse5_faz-6.4 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse5_faz-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse5_fct-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse5_fmg-6.4 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse5_fmg-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse6_fml-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse6_fnc-8.5 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse7_efw-6.4 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse7_efw-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse7_sac-6.2 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse7_sdw-6.4 dumps (pdf + vce)
fortinet nse8_811 dumps (pdf + vce)
This article is intended to help you pass the Simplifying Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) Cisco exam 300-410! Share some of the latest free 300-410 exam questions with the most comprehensive 300-410 enarsi dumps https://www.pass4itsure.com/300-410.html (PDF + VCE). I will update this article frequently to bring you the latest information on the Cisco 300-410 (ENARSI) exam.
Cisco CCNP 300-410 ENARSI Dumps
Cisco CCNP 300-410 ENARSI Exam
It’s a 90-minute exam that won’t be easy to pass! If you want to succeed in the 300-410 exam, you have to go through a lot of studies, or you can get 300-410 enarsi dumps from a well-known and reliable provider, recommend Pass4itSure.
As shown above, the Pass4itSure 300-410 enarsi dumps are suitable for the exam in every way. The price-performance ratio, trust are guaranteed.
Download 300-410 ENARSI Dumps PDF File:
CCNP ENARSI 300-410 dumps pdf [Drive] https://drive.google.com/file/d/1yPuoz2AsIepDiX6BE0Xmpu9kmhCrhlNW/view?usp=sharing
CCNP ENARSI 300-410 Dumps Some Questions [Test]
300-410 Q&As
QUESTION 1
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to connect to a device with SSH but cannot connect. The engineer connects by using the console and finds the displayed output when troubleshooting. Which command must be used in configuration mode to enable SSH on the device?

A. no IP ssh disable
B. IP ssh enable
C. IP ssh version 2
D. crypto key generate RSA
Correct Answer: D
QUESTION 2
Which protocol does MPLS use to support traffic engineering?
A. Tag Distribution Protocol
B. Resource Reservation Protocol
C. Border Gateway Protocol
D. Label Distribution Protocol
Correct Answer: B
MPLS TE provides a way to integrate TE capabilities (such as those used on Layer 2 protocols like ATM) into Layer 3 protocols (IP). MPLS TE uses an extension to existing protocols (Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS), Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP), OSPF) to calculate and establish unidirectional tunnels that are set according to the network constraint, Traffic flows are mapped on the different tunnels depending on their destination.
QUESTION 3
An engineer configured access list NON-CISCO in a policy to influence routes.

What are the two effects of this route map configuration? (Choose two.)
A. Packets are forwarded using normal route lookup.
B. Packets are forwarded to the default gateway.
C. Packets are dropped by the access list.
D. Packets are evaluated by sequence 10.
E. Packets are not evaluated by sequence 10.
Correct Answer: BD
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/ip-routed-protocols/47121-pbr-cmds-ce.html
QUESTION 4
Refer to the exhibit.
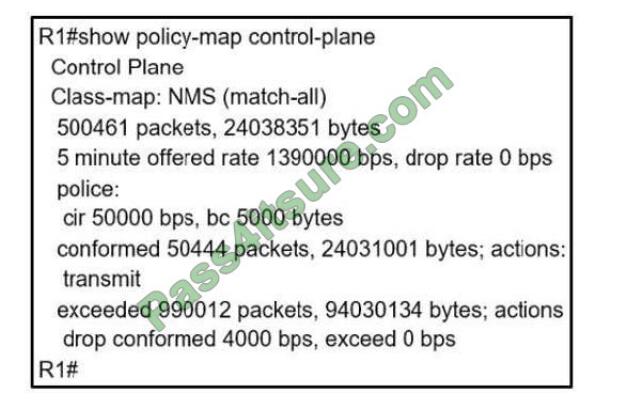
A company is evaluating multiple network management system tools. Trending graphs generated by SNMP data are returned by the NMS and appear to have multiple gaps. While troubleshooting the issue, an engineer noticed the relevant output.
What solves the gaps in the graphs?
A. Remove the exceed-rate command in the class map.
B. Remove the class-map NMS from being part of control plane policing.
C. Configure the CIR rate to a lower value that accommodates all the NMS tools
D. Separate the NMS class map in multiple class maps based on the specific protocols with appropriate CoPP actions
Correct Answer: D
The class-map NMS in the exhibit did not classify traffic into specific protocols so many packets were dropped. We should create a class map to classify the receiving traffic. It is also a recommendation of CoPP/CPP policy:
“Developing a CPP policy starts with the classification of the control plane traffic. To that end, the control plane traffic needs to be first identified and separated into different class maps.”
Reference: https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/resources/copp_best_practices
QUESTION 5
Which two statements about VRF-Lite configurations are true? (Choose two.)
A. They support the exchange of MPLS labels
B. Different customers can have overlapping IP addresses on different VPNs
C. They support a maximum of 512.000 routes
D. Each customer has its own dedicated TCAM resources
E. Each customer has its own private routing table.
F. They support IS-IS
Correct Answer: BE
QUESTION 6
When configuring Control Plane Policing on a router to protect it from malicious traffic, an engineer observes that the configured routing protocols start flapping on that device. Which action in the Control Plane Policy prevents this problem in a production environment while achieving the security objective?
A. Set the conform-action and exceed-action to transmit initially to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy in the output direction
B. Set the conform-action and exceed-action to transmit initially to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy in the input direction
C. Set the conform-action to transmit and exceed-action to drop to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy m the input direction
D. Set the conform-action to transmit and exceed-action to drop to test the ACLs and transmit rates and apply the Control Plane Policy m the output direction
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION 7
An engineer configured a leak-map command to summarize EIGRP routes and advertise specifically loopback 0 with an IP of 10.1.1.1.255.255.255.252 along with the summary route. After finishing the configuration, the customer complained about not receiving a summary route with specific loopback address.
Which two configurations will fix it? (Choose two.)

A. Configure access-list 1 permit 10.1.1.0.0.0.0.3.
B. Configure access-list 1 permit 10.1.1.1.0.0.0.252.
C. Configure access-list 1 and match under route-map Leak-Route.
D. Configure route-map Leak-Route permit 10 and match access-list 1.
E. Configure route-map Leak-Route permit 20.
Correct Answer: AD
When you configure an EIGRP summary route, all networks that fall within the range of your summary are suppressed and no longer advertised on the interface. Only the summary route is advertised. But if we want to advertise a network that has been suppressed along with the summary route then we can use the leak-map feature. The below commands will fix the configuration in this question: R1(config)#access-list 1 permit 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 R1(config)#route-map Leak-Route permit 10 // this command will also remove the “route_map Leak-Route deny 10” command. R1(config-route-map)#match IP address 1
QUESTION 8
DRAG-DROP
Drag and drop the SNMP attributes in Cisco IOS devices from the left onto the correct SNMPv2c or SNMPV3 categories on the right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
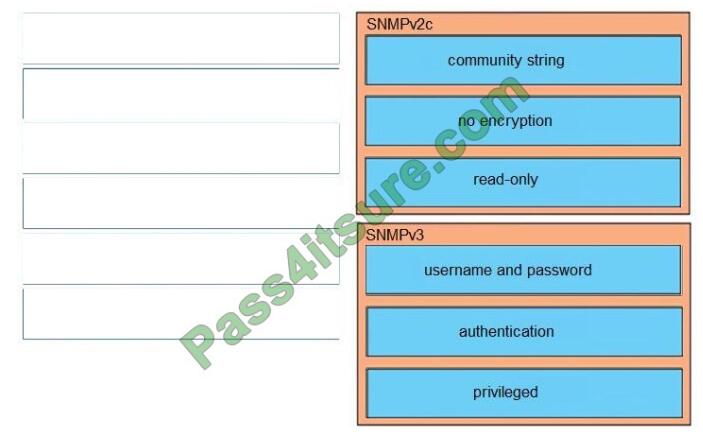
SNMPv2c:
+
community string
+
no encryption
+
read-only SNMPv3:
+
username and password
+
authentication
+
privileged
QUESTION 9
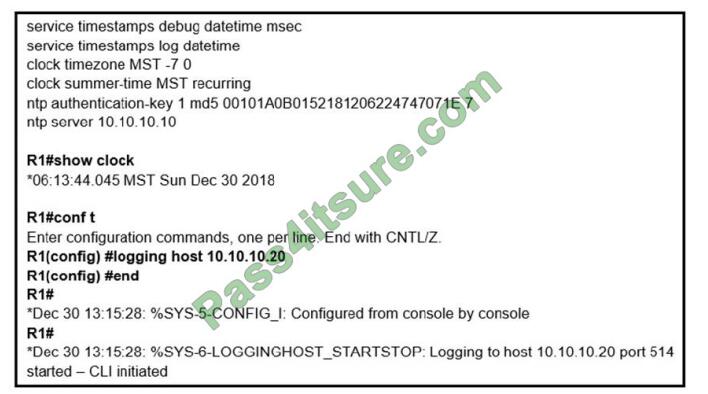
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator noticed that after a change was made on R1, the timestamps on the system logs did not match the clock. What is the reason for this error?
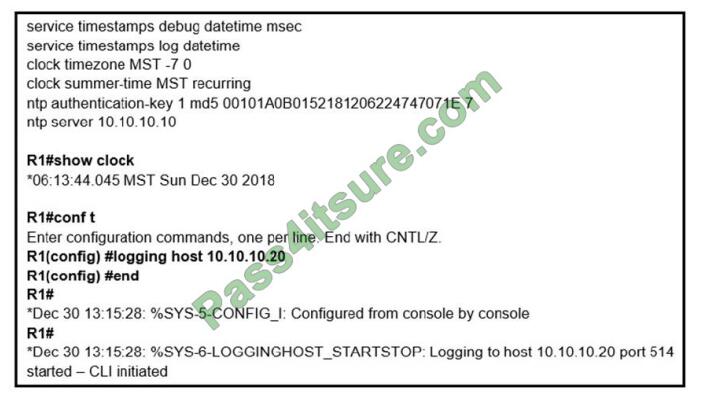
A. An authentication error with the NTP server results in an incorrect timestamp.
B. The keyword local time is not defined on the timestamp service command.
C. The NTP server is in a different time zone.
D. The system clock is set incorrectly to summer-time hours.
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION 10
Which statement about IPv6 RA Guard is true?
A. It does not offer protection in environments where IPv6 traffic is tunneled.
B. It cannot be configured on a switch port interface in the ingress direction.
C. Packets that are dropped by IPv6 RA Guard cannot be spanned.
D. It is not supported in hardware when TCAM is programmed.
Correct Answer: A
Restrictions for IPv6 RA Guard
The IPv6 RA Guard feature does not offer protection in environments where IPv6 traffic is tunneled.
This feature is supported only in hardware when the ternary content addressable memory (TCAM) is programmed.
This feature can be configured on a switch port interface in the ingress direction.
This feature supports host mode and router mode.
This feature is supported only in the ingress direction; it is not supported in the egress direction.
This feature is not supported on EtherChannel and EtherChannel port members.
This feature is not supported on trunk ports with merge mode.
This feature is supported on auxiliary VLANs and private VLANs (PVLANs). In the case of PVLANs, primary VLAN features are inherited and merged with port features.
Packets dropped by the IPv6 RA Guard feature can be spanned.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/ipv6_fhsec/configuration/xe-16/ip6f-xe-16-book/ip6-ra-guard.pdf
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/ipv6_fhsec/configuration/xe-3s/ip6f-xe-3s-book/ip6-ra-guard.pdf
QUESTION 11
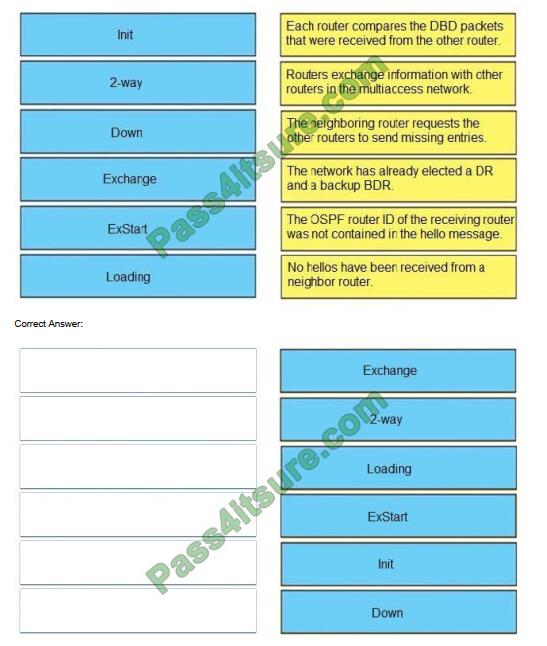
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the OSPF adjacency states from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Select and Place:

Down
This is the first OSPF neighbor state. It means that no information (hellos) has been received from this neighbor, but hello packets can still be sent to the neighbor in this state. During the fully adjacent neighbor state, if a router doesn\\’t receive a hello packet from a neighbor within the Router Dead Interval time (RouterDeadInterval = 4*HelloInterval by default) or if the manually configured neighbor is being removed from the configuration, then the neighbor state changes from Full to Down.
Attempt
This state is only valid for manually configured neighbors in an NBMA environment. In Attempt state, the router sends unicast hello packets every poll interval to the neighbor, from which hellos have not been received within the dead interval.
Init
This state specifies that the router has received a hello packet from its neighbor, but the receiving router\\’s ID was not included in the Hello packet. When a router receives a hello packet from a neighbor, it should list the sender\\’s router ID in its hello packet as an acknowledgment that it received a valid hello packet.
2-Way
This state designates that bi-directional communication has been established between two routers. Bi-directional means that each router has seen the other\\’s hello packet. This state is attained when the router receiving the hello packet sees its own Router ID within the received hello packet\\’s neighbor field.
At this state, a router decides whether to become adjacent with this neighbor. On broadcast media and non-broadcast multiaccess networks, a router becomes full only with the designated router (DR) and the backup designated router (BDR); it stays in the 2-way state with all other neighbors.
On Point-to-point and Point-to-multipoint networks, a router becomes full with all connected routers.
At the end of this stage, the DR and BDR for broadcast and non-broadcast multiaccess networks are elected. For more information on the DR election process, refer to DR Election.
Note: Receiving a Database Descriptor (DBD) packet from a neighbor in the init state will also cause a transition to a 2-way state.
Extract
Once the DR and BDR are elected, the actual process of exchanging link-state information can start between the routers and their DR and BDR. (ie. Shared or NBMA networks). In this state, the routers and their DR and BDR establish a master-slave relationship and choose the initial sequence number for adjacency formation.
The router with the higher router ID becomes the master and starts the exchange, and as such, is the only router that can increment the sequence number. Note that one would logically conclude that the DR/BDR with the highest router ID will become the master during this process of master-slave relation.
Remember that the DR/BDR election might be purely by virtue of a higher priority configured on the router instead of the highest router ID. Thus, it is possible that a DR plays the role of slave. And also note that master/slave election is on a per-neighbor basis.
Exchange
In the exchange state, OSPF routers exchange database descriptor (DBD) packets. Database descriptors contain link state advertisement (LSA) headers only and describe the contents of the entire link-state database. Each DBD packet has a sequence number that can be incremented only by the master which is explicitly acknowledged by the slave.
Routers also send link-state request packets and link-state update packets (which contain the entire LSA) in this state. The contents of the DBD received are compared to the information contained in the router’s link-state database to check if new or more current link-state information is available with the neighbor.
Loading In this state, the actual exchange of link-state information occurs.
Based on the information provided by the DBDs, routers send link-state request packets. The neighbor then provides the requested link-state information in link-state update packets. During the adjacency, if a router receives an outdated or missing LSA, it requests that LSA by sending a link-state request packet. All link-state update packets are acknowledged.
Full
In this state, routers are fully adjacent to each other. All the router and network LSAs are exchanged and the routers\\’ databases are fully synchronized. Full is the normal state for an OSPF router. If a router is stuck in another state, it is an indication that there are problems in forming adjacencies.
The only exception to this is the 2-way state, which is normal in a broadcast network. Routers achieve the FULL state with their DR and BDR in NBMA/broadcast media and FULL state with every neighbor in the remaining media such as point-to-point and point-to-multipoint.
Note: The DR and BDR that achieve a FULL state with every router on the segment will display FULL/BROTHER when you enter the show IP OSPF neighbor command on either a DR or BDR. This simply means that the neighbor is not a DR or BDR, but since the router on which the command was entered is either a DR or BDR, this shows the neighbor as FULL/BROTHER.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13685-13.html
+
Each router compares the DBD packets that were received from the other router: Exchange
+
Routers exchange information with other routers in the multiaccess network: Exstart
+
The neighboring router requests the other routers to send missing entries: Loading
+
The network has already elected a DR and a backup BDR: 2-way
+
The OSPF router ID of the receiving router was not contained in the hello message: Init
+
No hellos have been received from a neighbor router: Down
When OSPF adjacency is formed, a router goes through several state changes before it becomes fully adjacent with its neighbor.
The states are Down -> Attempt (optional) -> Init -> 2-Way -> Exstart -> Exchange -> Loading -> Full. Short descriptions about these states are listed below:
Down: no information (hellos) has been received from this neighbor. Attempt: only valid for manually configured neighbors in an NBMA environment. In Attempt state, the router sends unicast hello packets every poll interval to the neighbor, from which hellos have not been received within the dead interval.
Init: specifies that the router has received a hello packet from its neighbor, but the receiving router\\’s ID was not included in the hello packet
2-Way: indicates bi-directional communication has been established between two routers.
Extract: Once the DR and BDR are elected, the actual process of exchanging link-state information can start between the routers and their DR and BDR.
Exchange: OSPF routers exchange and compare database descriptor (DBD) packets Loading: In this state, the actual exchange of link-state information occurs. Outdated or missing entries are also requested to be resent.
Full: routers are fully adjacent with each other
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080093f0e.shtml
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13685-13.html Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13685-13.html
QUESTION 12
Refer to the exhibit. The DHCP client is unable to receive an IP address from the DHCP server. RouterB is configured as follows:
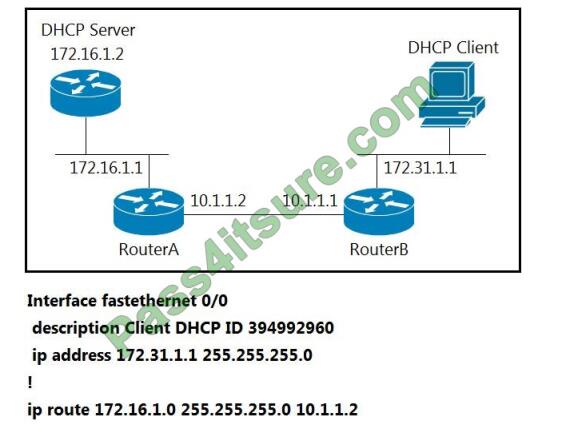
Which command is required on the FastEthernet 0/0 interface of RouterB to resolve this issue?
A. RouterB(config-if)#lp helper-address 172.31.1.1
B. RouterBiconfig-ififclp helper-address 255.255 255 255
C. RouterB(config-if)#lp helper-address 172.16.1.1
D. RouterB(config-if)#lp helper-address 172.16.1.2
Correct Answer: D
The CCNP 300-410 exam provides the next step for individuals looking to improve their level of skill and helps meet the growing demand for Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services professionals. Passing the exam is necessary! Above I have already answered how to pass. All you need to do to continue is to continue practicing the exam questions.
For the full CCNP 300-410 ENARSI Dumps (PDF + VCE) click here https://www.pass4itsure.com/300-410.html
Other related CCNP https://www.exampass.net/category/ccnp
Written by Ralph K. Merritt
We are here to help you study for Cisco certification exams. We know that the Cisco series (CCNP, CCDE, CCIE, CCNA, DevNet, Special and other certification exams are becoming more and more popular, and many people need them. In this era full of challenges and opportunities, we are committed to providing candidates with the most comprehensive and comprehensive Accurate exam preparation resources help them successfully pass the exam and realize their career dreams. The Exampass blog we established is based on the Pass4itsure Cisco exam dump platform and is dedicated to collecting the latest exam resources and conducting detailed classification. We know that the most troublesome thing for candidates during the preparation process is often the massive amount of learning materials and information screening. Therefore, we have prepared the most valuable preparation materials for candidates to help them prepare more efficiently. With our rich experience and deep accumulation in Cisco certification, we provide you with the latest PDF information and the latest exam questions. These materials not only include the key points and difficulties of the exam, but are also equipped with detailed analysis and question-answering techniques, allowing candidates to deeply understand the exam content and master how to answer questions. Our ultimate goal is to help you study for various Cisco certification exams, so that you can avoid detours in the preparation process and get twice the result with half the effort. We believe that through our efforts and professional guidance, you will be able to easily cope with exam challenges, achieve excellent results, and achieve both personal and professional improvement. In your future career, you will be more competitive and have broader development space because of your Cisco certification.
Categories
2025 Microsoft Top 20 Certification Materials
- Microsoft Azure Administrator –> az-104 dumps
- Microsoft Azure Fundamentals –> az-900 dumps
- Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure –> dp-203 dumps
- Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure –> az-204 dumps
- Microsoft Power Platform Developer –> pl-400 dumps
- Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution –> ai-102 dumps
- Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst –> pl-300 dumps
- Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions –> az-400 dumps
- Microsoft Azure Security Technologies –> az-500 dumps
- Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect –> sc-100 dumps
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Customer Engagement Apps (CRM) –> mb-910 dumps
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Finance and Operations Apps (ERP) –> mb-920 dumps
- Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals –> dp-900 dumps
- Microsoft 365 Fundamentals –> ms-900 dumps
- Microsoft Security Compliance and Identity Fundamentals –> sc-900 dumps
- Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals –> ai-900 dumps
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Solution Architect –> mb-700 dumps
- Microsoft 365 Certified: Enterprise Administrator Expert –> ms-102 dumps
- Microsoft 365 Certified: Collaboration Communications Systems Engineer Associate –> ms-721 dumps
- Endpoint Administrator Associate –> md-102 dumps

